You are the average of the five people you most associate with
Imagine you are a teacher at a prestigious school, and a new student applies for admission. As someone who enjoys making predictions, you want to determine whether the applicant will be selected. Before the admission process, the school collects various attributes about each applicant through evaluations and their academic and personal history. Drawing from your experience on the admission panel, you can assess the applicant based on these attributes.
One approach is to compare the applicant with all other applicants and identify the five most similar individuals based on their attributes. Let's assume that out of these five applicants, four were selected and one was not. Intuitively, you can predict that the new student will be selected. Even if three out of five were selected, you can still assume a high chance of selection. So, what we are actually doing is taking the mode of the selection label among the 5 closest applicants and classifying the applicant accordingly. This algorithm is known as k-nearest neighbor classification, with a value of k set to 5 in this example.
Now, let's consider predicting the applicant's score on the selection test. One possible approach is to find the top five applicants who are most similar to the target applicant, as we did in the previous example, and compute the average score of these applicants. This algorithm is called k-nearest neighbor regression, with a value of k set to 5 in this case.
Both of these algorithms fall under the category of k-nearest neighbors (k-NN) algorithm, which is one of the simplest machine learning methods.
To determine the similarity between two observations, we compute the distance between them using a distance metric such as the Euclidean distance.
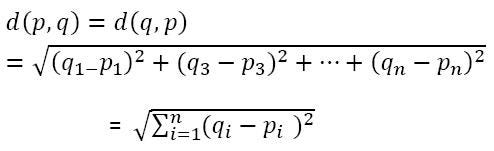 Image Source: Imgur
Image Source: Imgur
Here, pi represents the value of the i-th feature in the first observation, and qi represents the value of the i-th feature in the second observation.
When k=1, the algorithm is known as the nearest neighbor algorithm, and the label of the nearest neighbor is assigned to the observation.
It is crucial to select an appropriate value for k that neither too high nor too low, depending on the data. If k is too high, the model will not generalize well and will predict the same value in most cases. For example, setting k=n (the number of samples in the training set) will result in all predictions being equal to the mode of the training set. On the other hand, if k is too small, the model may fail to filter out outliers effectively.
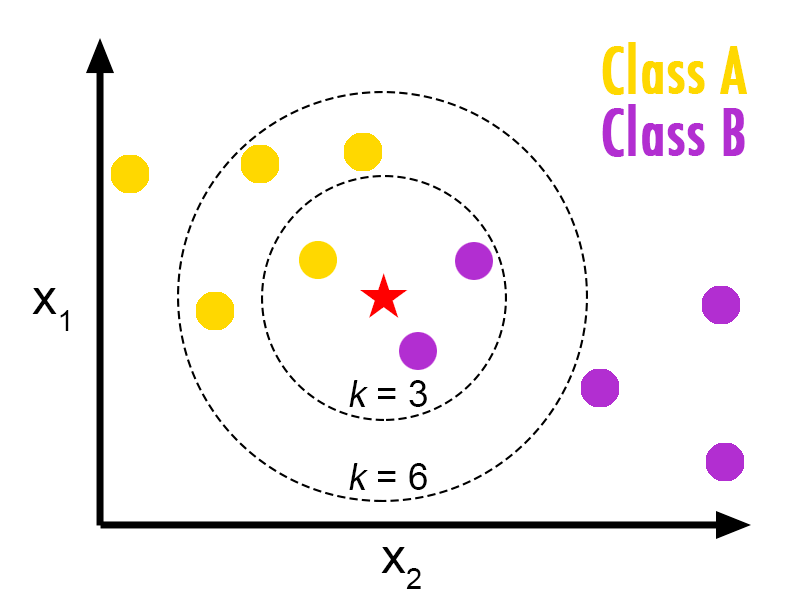 Image Source: en.proft.com.ua
Image Source: en.proft.com.ua
One drawback of using k-NN is that, for example, when k=7 and the three nearest neighbors are labeled 'x' while the next four are labeled 'y', the algorithm will predict 'y' even though intuitively, it should have been 'x'. This issue can be addressed by assigning more weight to the nearest neighbors and reducing the weight as we move farther away.
Similarly, when the dataset is skewed, the mode will often belong to the majority class even if it is distant from the target. To mitigate this, we can use weights based on the inverse of the distance.
The k-NN classifier is available in scikit-learn as the KNeighborsClassifier in the sklearn.neighbors module, while the k-NN regressor is available as KNeighborsRegressor in the same module.